1. Introduction to Bank Nifty
Bank Nifty, officially known as the Nifty Bank Index, is one of India’s most popular and widely traded stock indices. It tracks the performance of the 12 largest and most liquid banks listed on the National Stock Exchange (NSE).
Unlike broader indices like Nifty 50 or Sensex, Bank Nifty is sector-specific, focusing exclusively on the banking sector. As such, it serves as a barometer of India’s financial sector health and is often the first index traders and investors look at to gauge banking market sentiment.
Why Bank Nifty Matters
- High liquidity: Easy for traders and institutions to enter and exit positions
- Derivative-friendly: Futures and options are widely available
- Market sentiment indicator: Moves often reflect broader economic and RBI policies
- Portfolio tool: Used for hedging or sector-focused investments
2. Components of Bank Nifty
Bank Nifty is composed of 12 major banking stocks that represent a mix of public sector banks (PSUs) and private banks #BankNifty.
Current Major Constituents
- HDFC Bank
- ICICI Bank
- Kotak Mahindra Bank
- State Bank of India (SBI)
- Axis Bank
- IndusInd Bank
- Bank of Baroda
- Punjab National Bank
- Union Bank of India
- IDFC First Bank
- Federal Bank
- Yes Bank
Pro Tip: The index weights are based on free-float market capitalization, meaning larger banks like HDFC Bank and ICICI Bank have a bigger influence on the Bank Nifty movement #IndianBanks.
3. How Bank Nifty Differs from Nifty 50 and Sensex
| Index | Focus | Constituents | Volatility | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bank Nifty | Banking sector | 12 major banks | High | Traders, banking sector investors |
| Nifty 50 | Top 50 companies across sectors | 50 large-cap companies | Medium | Long-term investors |
| Sensex | Top 30 BSE-listed companies | 30 large-cap companies | Medium | Benchmark for market trends |
Bank Nifty moves more aggressively than Nifty 50, especially during RBI policy announcements, banking news, or economic changes affecting interest rates. Midcap indices, on the other hand, can show even higher volatility but are less connected to banking trends.
4. Key Drivers of Bank Nifty Movements
Bank Nifty is highly sensitive to several domestic and international factors. Understanding these drivers is essential for both traders and long-term investors.
4.1 RBI Monetary Policy
- Repo rate changes
- Cash reserve ratio (CRR) adjustments
- Liquidity measures
Bank Nifty responds immediately to interest rate changes, making it an excellent gauge of monetary policy impact.
4.2 FII Flows
Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) heavily trade in Bank Nifty.
- FII inflows → upward momentum
- FII outflows → downward pressure
4.3 Earnings of Constituent Banks
Quarterly results of top banks can significantly affect the index. Large profit announcements often push Bank Nifty higher, while bad news can trigger sharp declines.
4.4 Government Policies
- PSU recapitalization
- Bank mergers
- Regulatory changes
Example: Announcements on merger of public sector banks often create short-term market volatility.
4.5 Domestic and Global Market Sentiment
- Crude oil price changes affecting PSU banks
- US Fed rate decisions
- Global banking trends
Even if other sectors are stable, Bank Nifty can react strongly to sector-specific global cues.
5. Advantages of Bank Nifty
- Sector-Specific Focus: Provides clear insights into banking sector health.
- High Liquidity: Futures and options are among the most actively traded.
- Derivatives Opportunities: Ideal for hedging and speculation.
- Portfolio Diversification: Offers banking exposure without picking individual stocks.
- Predictable Policy Response: Moves often follow RBI announcements.
6. Disadvantages of Bank Nifty
- High Volatility: Prices can swing sharply in short periods.
- Sector Concentration: Lack of diversification increases risk.
- Policy Sensitivity: Highly responsive to interest rates and regulatory changes.
- Not Beginner-Friendly: Requires experience or professional guidance for trading futures/options.
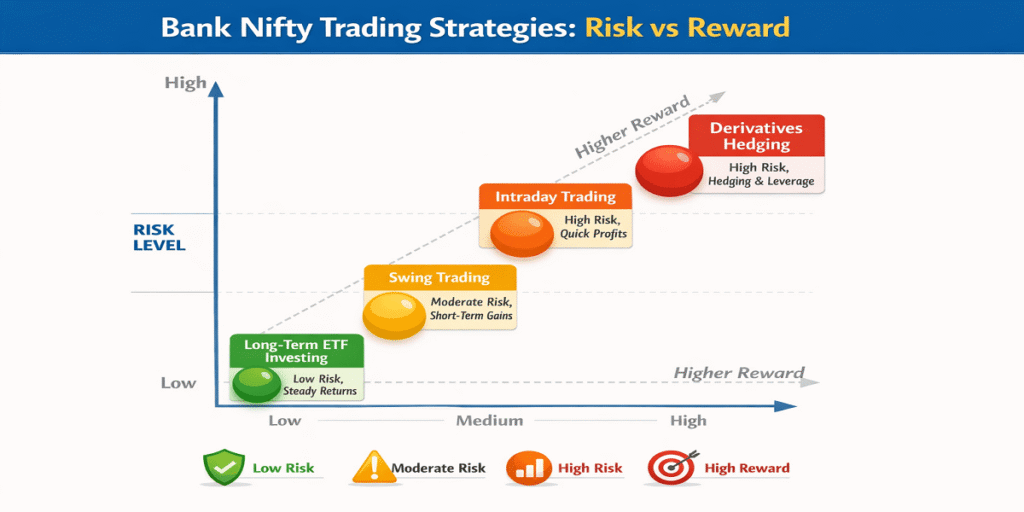
7. Trading & Investment Strategies
7.1 Long-Term Investment
- Use Bank Nifty ETFs or Index Funds
- Ideal for investors looking for sector-focused growth
- Lower risk than individual bank stocks
7.2 Short-Term Trading
- Futures and options provide intraday and swing trading opportunities
- High liquidity makes quick entries and exits possible
7.3 Hedging Strategies
- Investors with large equity portfolios use Bank Nifty derivatives to hedge exposure to the financial sector.
Tip: Always combine Bank Nifty strategies with Nifty 50 to balance risk and reward.
8. Bank Nifty vs Nifty Financial Services Index
- Bank Nifty: Pure banking sector → 12 banks
- Nifty Financial Services: Banking + insurance + NBFCs + other financial companies
Bank Nifty reacts faster to interest rate changes while Nifty Financial Services provides a more diversified financial sector view.
9. Historical Performance of Bank Nifty
- Historically, Bank Nifty has outperformed Nifty 50 during economic expansions.
- In bear markets, it falls faster due to sector concentration.
- Investors should track interest rate cycles and government announcements to anticipate movement.
10. How Global Events Affect Bank Nifty
- FII flows in/out of India
- US Fed rate decisions and banking sector trends
- Crude oil price movements affecting PSU banks
- Global financial stability and banking crises
Bank Nifty vs Sector ETFs
| Instrument | Focus | Risk | Liquidity | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bank Nifty ETF | 12 banks | Medium-High | High | Long-term banking exposure |
| Nifty Financial Services ETF | Banks + NBFCs + Insurance | Medium | Medium | Diversified financial sector |
| Midcap Banking ETFs | Medium-sized banks | High | Medium | Aggressive investors |
FAQ Section
Is Bank Nifty suitable for beginners?
Beginners should prefer ETFs or SIPs; derivatives are risky.
How often is Bank Nifty reviewed?
Twice a year based on liquidity and market capitalization.
What drives Bank Nifty the most?
RBI policies, FII flows, earnings, and government reforms.
Can Bank Nifty outperform Nifty 50?
Yes, during bullish banking cycles, but risk is higher.
What is the best way to trade Bank Nifty?
Combination of technical analysis, fundamental tracking, and risk management.
Are Bank Nifty ETFs safe?
Yes, ETFs provide diversified exposure with lower risk than futures/options.
Disclaimer
The content on this page is for educational and informational purposes only and should not be considered as financial, investment, or trading advice. Bank Nifty trading, futures, and options involve high risk, and past performance does not guarantee future results. Always consult a licensed financial advisor before making any investment or trading decisions. The website and authors are not responsible for any losses incurred based on the information provided here.
Source of data: National Stock Exchange (NSE), official Bank Nifty publications, and public financial data.